Chapter 3: Understanding the CSS Box Model
The CSS Box Model is a fundamental concept in web design and layout. It defines how elements are structured and how their dimensions are calculated, including their content, padding, border, and margin. Understanding the Box Model is crucial for creating well-designed and responsive web layouts.
Components of the Box Model
Each element on a web page is represented as a rectangular box, which consists of the following components:
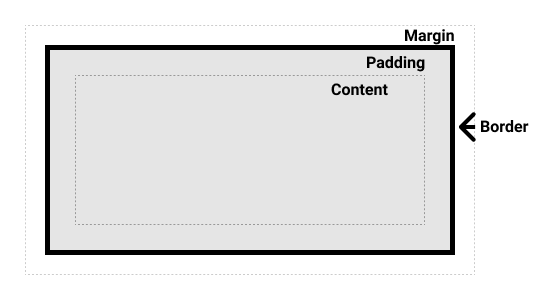
- Content: The innermost part of the box, where text and images appear.
- Padding: Space between the content and the border. It is inside the element and increases the element's size.
- Border: Surrounds the padding and content. It defines the element's boundary.
- Margin: The outermost space around the border. It separates the element from other elements and is outside the element's box.
Box Model Diagram
Properties of the Box Model
1. Content
The content area is where the actual content of the box is displayed. Its size is determined by the width and height properties.
Example:
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
}
HTML:
<div class="box">Content Area</div>
2. Padding
Padding is the space between the content and the border. It can be set for all sides or individually for each side.
Properties:
padding: Sets padding for all sides.padding-top: Sets padding for the top.padding-right: Sets padding for the right.padding-bottom: Sets padding for the bottom.padding-left: Sets padding for the left.
Example:
.box {
padding: 20px;
}
HTML:
<div class="box">Content with Padding</div>
3. Border
Borders are lines surrounding the padding (and content). They can be styled with color, width, and style.
Properties:
border: Sets border for all sides.border-width: Sets the width of the border.border-style: Sets the style of the border (e.g.,solid,dashed,dotted).border-color: Sets the color of the border.
Example:
.box {
border: 2px solid black;
}
HTML:
<div class="box">Content with Border</div>
4. Margin
Margin is the space outside the border, separating the element from other elements. It can be set for all sides or individually.
Properties:
margin: Sets margin for all sides.margin-top: Sets margin for the top.margin-right: Sets margin for the right.margin-bottom: Sets margin for the bottom.margin-left: Sets margin for the left.
Example:
.box {
margin: 30px;
}
HTML:
<div class="box">Content with Margin</div>
Box Model Calculations
When calculating the total width and height of an element, consider the following:
- Width Calculation:
width = content width + padding left + padding right + border left + border right + margin left + margin right - Height Calculation:
height = content height + padding top + padding bottom + border top + border bottom + margin top + margin bottom
Box-Sizing Property
The box-sizing property allows you to control how the width and height of an element are calculated.
content-box(default): Width and height apply to the content only, and padding and border are added outside.border-box: Width and height include padding and border, making the total size of the box equal to the specified width and height.
Example:
.box {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 200px;
padding: 20px;
border: 2px solid black;
}
Explanation: With box-sizing: border-box, the total width of .box will be 200px, including padding and border.
Practical Examples
Example 1: Basic Box Model
CSS:
.box {
width: 150px;
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
border: 5px solid blue;
margin: 20px;
background-color: lightgray;
}
HTML:
<div class="box">Box with Padding, Border, and Margin</div>
Example 2: Box-Sizing Property
CSS:
.box {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 150px;
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
border: 5px solid blue;
background-color: lightgray;
}
HTML:
<div class="box">Box with Border-Box Sizing</div>